A Strategic Review on Use of Polyhydroxyalkanoates as an Immunostimulant in Aquaculture
Applied Food Biotechnology,
Vol. 8 No. 1 (2021),
14 December 2020,
Page 1-18
https://doi.org/10.22037/afb.v8i1.31255
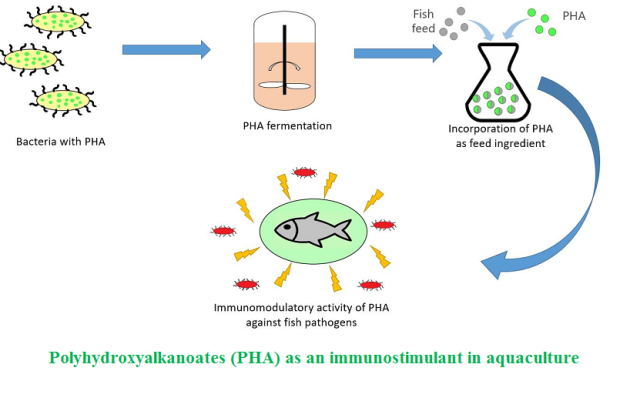
Background and Objective: Increasing concerns over the use of antibiotics in aquaculture have emerged researchers to focus on short chain fatty acids and other biocompatible molecules as alternatives for disease prophylaxis and treatment. Polyhydroxyalkanoates well studied as biopolymeric materials for using in packaging and biomedicine were not focused much for their abilities to act as antimicrobial agents in aquaculture until recent years. Application studies of polyhydroxyalkanoates as aquafeed additives have highlighted their promising roles as eco-friendly alternatives for commercial antibiotics with strong immunomodulatory effects in fish-es and shrimps. The major aim of this review was to explore up-to-date scientific research studies on use of polyhydroxyalkanoates as aquafeed additives and their immunomodulatory effects.
Results and Conclusion: Up-to-date, limited scientific literatures have been published on the use of polyhydroxyalkanoates and their copolymers as alternatives to antibiotics in aquaculture. This research field includes a great scope of development due to the promising immu-nomodulatory and antimicrobial activity of polyhydroxyalkanoates against common pathogens in aquaculture, as reported in literatures. Although several hypothesis and research data for explaining the mechanisms behind their immunostimulatory effects were suggested by various researchers, genetic and molecular bases underlying these phenomena are yet to be explored. Further research and development in this area can introduce these biopolymers as the most promising eco-friendly alternatives for antibiotics in aquaculture.
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest

.png)