Process Optimization and Characterization of Enhanced Vanillin Yield Using Bacillus aryabhattai NCIM 5503
Applied Food Biotechnology,
Vol. 8 No. 2 (2021),
16 March 2021
,
Page 113-119
https://doi.org/10.22037/afb.v8i2.32913
Abstract
Background and Objective:
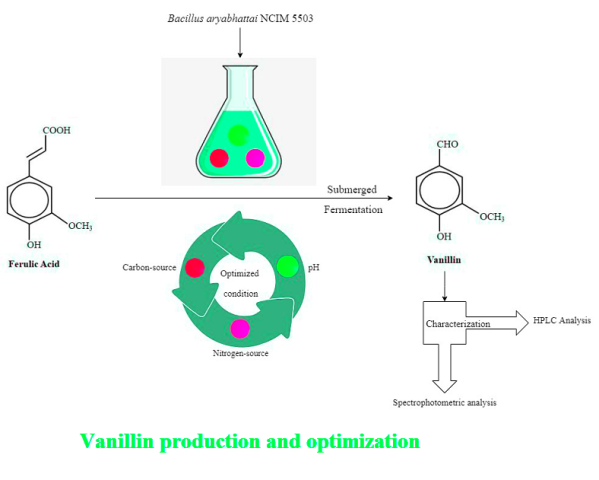
Vanillin is a strong flavor used widely in food industries, but the quantity of this compound from plant sources is minimal. In the present study, vanillin was produced as bio-vanillin using biotechnological techniques and effects of the process parameters (carbon-source, nitrogen-source and pH) on ferulic acid bioconversion to vanillin for enhancing vanillin concentration were studied using Bacillus aryabhattai NCIM 5503.
Material and Methods:
Briefly, culture media included 5 g l-1 each carbon (glucose, sucrose, fructose, sorbitol, lactose, xylitol and mannitol) and nitrogen (ammonium sulphate, peptone, beef extract, yeast extract and urea) sources in distilled water supplemented with 5% (w v‑1) of ferulic acid and 1% (v v-1) of Bacillus aryabhattai NCIM 5503 as inoculum at a pH range of 4.5-12. Fermentation broth was extracted using centrifuge and further analyzed for the presence of vanillin using spectrophotometry and high-performance liquid chromatography.
Results and conclusion:
This study revealed that a maximum vanillin concentration of 0.87 g l-1 was achieved under optimum conditions (culture media with fructose and beef extract at pH 9) of 30 ºC and 150 rpm. Furthermore, vanillin in the extracted fermented broth was characterized using high-performance liquid chromatography and spectrophotometric analysis with thiobarbituric acid assay at 55 ºC for 10 min followed by 20 min of incubation at room temperature.
- ▪ Bioconversion
- ▪ Bacillus aryabhattai
- ▪ Ferulic acid
- ▪ Fructose
- ▪ Submerged fermentation
- ▪ Vanillin
How to Cite
References
Ashengroph M, Nahvi I, Zarkesh-Esfahani H. A bioconversion process using a novel isolated strain of Pseudomonas sp. ISPC2 to produce natural vanillin from isoeugenol. Res Pharm Sci. 2009; 3(2): 41-47.
Converti A, Aliakbarian B, Dominguez JM, Vazquez GB, Perego P. Microbial production of biovanillin. Braz J Micro-biol. 2010; 41(3): 519-530.
doi:10.1590/S1517-83822010000300001
Singh A, Mukhopadhyay K, Ghosh Sachan S. Biotrans-formation of eugenol to vanillin by a novel strain Bacillus safensis SMS1003. Biocatal Biotransformation. 2019; 37(4): 291-303.
doi: 10.1080/10242422.2018.1544245
Galadima AI, Salleh MM, Hussin H, Chong CS, Yahya A, Mohamad SE, Abd-Aziz S, Yusof NNM, Naser MA, Al-Junid AFM. Biovanillin: Production concepts and prevention of side product formation. Biomass Convers Biorefinery. 2020; 10(2): 589-609.
doi:10.1007/s13399-019-00418-0
Furuya T, Kuroiwa M, Kino K. Biotechnological production of vanillin using immobilized enzymes. J Biotechnol. 2017; 243: 25-28.
doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.12.021
Zhao LQ, Sun ZH, Zheng P, Zhu LL. Biotransformation of isoeugenol to vanillin by a novel strain of Bacillus fusiformis. Biotechnol Lett. 2005; 27(19): 1505-1509.
doi:10.1007/s10529-005-1466-x
Kaur B, Chakraborty D. Biotechnological and molecular approaches for vanillin production: A review. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2013; 169(4): 1353-1372.
doi:10.1007/s12010-012-0066-1
Perez-Rodriguez N, de Souza Oliveira RP, Agrasar AMT, Dominguez JM. Ferulic acid transformation into the main vanilla aroma compounds by Amycolatopsis sp. ATCC 39116. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016; 100(4): 1677-1689.
doi: 10.1007/s00253-015-7005-3
Achterholt S, Priefert H, Steinbuchel A. Identification of Amycolatopsis sp. strain HR167 genes, involved in the bioconversion of ferulic acid to vanillin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2000; 54(6): 799-807.
doi: 10.1007/s002530000431
Chen P, Yan L, Wu Z, Li S, Bai Z, Yan X, Wang N, Liang N, Li H. A microbial transformation using Bacillus subtilis B7-S to produce natural vanillin from ferulic acid. Sci Rep. 2016; 6: 20400.
doi: 10.1038/srep20400
Kaur B, Chakraborty D, Kumar B. Phenolic biotrans-formations during conversion of ferulic acid to vanillin by lactic acid bacteria. Biomed Res Int. 2013; 2013:2-6.
doi:10.1155/2013/590359
Gunnarsson N, Palmqvist EA. Influence of PH and Carbon Source on the Production of Vanillin from Ferulic Acid by Streptomyces setonii ATCC 39116. In: Developments in Food Science. Elsevier; 2006; 73-76.
doi: 10.1016/S0167-4501(06)80018-X
Paz A, Outeirino D, Oliveira RP de S, Dominguez JM. Fed-batch production of vanillin by Bacillus aryabhattai BA03. New Biotechnol. 2018; 40: 186-191.
doi:10.1016/j.nbt.2017.07.012
Rana R, Mathur A, Jain CK, Sharma SK, Mathur G. Microbial production of vanillin. Int J Biotechnol Bioeng Res. 2013; 4(3): 227-234.
Yan L, Chen P, Zhang S, Li S, Yan X, Wang N, Liang N, Li H. Biotransformation of ferulic acid to vanillin in the packed bed-stirred fermentors. Sci Rep. 2016; 6(1): 1-12.
doi: 10.1038/srep34644
Oddou JC, Stentelaire C, Lesage-Meessen L, Asther M, Ceccaldi BC. Improvement of ferulic acid bioconversion into vanillin by use of high-density cultures of Pycnoporus cinnab-arinus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1999; 53(1): 1-6.
doi: 10.1007/s002530051605
Chakraborty D, Kaur B, Obulisamy K, Selvam A, Wong JWC. Agrowaste to vanillin conversion by a natural Pediococcus acidilactici strain BD16. Environ Technol. 2017; 38(13-14): 1823-1834.
doi: 10.1080/09593330.2016.1237556
He XY, Liu JX, Cao XH, Ye YZ. The study and application of determination of vanillin by spectrophotometry with thiobarbi-turic acid. Anal Lab Beijing. 1999; 18: 56-58.
Tilay A, Bule M, Annapure U. Production of biovanillin by one-step biotransformation using fungus Pycnoporous cinna-barinus. J Agric Food Chem. 2010; 58(7): 4401-4405.
doi: 10.1021/jf904141u
Yoon SH, Li C, Lee YM, Lee SH, Kim SH, Choi MS, Seo WT, Yang JK, Kim JY, Kim SW. Production of vanillin from ferulic acid using recombinant strains of Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng. 2005;10 (4): 378-384.
doi: 10.1007/BF02931859
Hua D, Ma C, Song L, Lin S, Zhang Z, Deng Z, Xu P. Enhanced vanillin production from ferulic acid using adsorbent resin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007; 74(4): 783-790.
doi:10.1007/s00253-006-0735-5
Paz A, Carballo J, Perez MJ, Dominguez JM. Bacillus aryabhattai BA03: A novel approach to the production of natural value-added compounds. World J Microbiol Biote-chnol. 2016; 32(10): 159.
doi: 10.1007/s11274-016-2113-5
Mazhar B, Jahan N, Mazhar Ali N, Andleeb S, Ali S. Production of vanillin by a novel bacterium from waste residues of rice bran oil. Punjab Univ J Zool. 2017; 32(1): 137- 142.
Zhao LQ, Sun ZH, Zheng P, He JY. Biotransformation of isoeugenol to vanillin by Bacillus fusiformis CGMCC1347 with the addition of resin HD-8. Process Biochem. 2006; 41(7): 1673-1676.
doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2006.02.007
Ma X, Daugulis AJ. Transformation of ferulic acid to vanillin using a fed‐batch solid-liquid two-phase partitioning bioreactor. Biotechnol Prog. 2014; 30(1): 207-214. doi:10.1002/btpr.1830
Motedayen N, Ismail MBT, Nazarpour F. Bioconversion of ferulic acid to vanillin by combined action of Aspergillus niger K8 and Phanerochaete crysosporium ATCC 24725. Afr J Biotechnol. 2013; 12(47): 6618-6624.
doi: 10.5897/AJB2013.12416
Muheim A, Lerch K. Towards a high-yield bioconversion of ferulic acid to vanillin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1999; 51(4): 456-461.
doi: 10.1007/s002530051416
- Abstract Viewed: 584 times
- pdf Downloaded: 590 times
