Designing a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Nanomembrane for the Selective Removal of Staphylococcus aureus from Aqueous Media
Applied Food Biotechnology,
Vol. 8 No. 4 (2021),
2 October 2021
,
Page 275-284
https://doi.org/10.22037/afb.v8i4.35279
Abstract
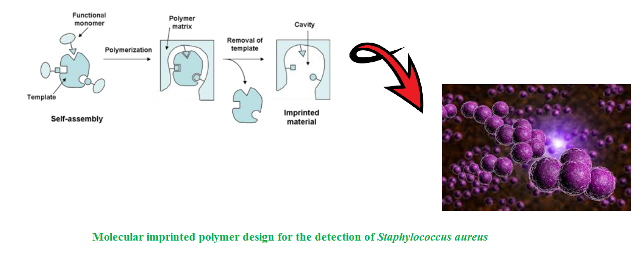
Background and Objective: Conventional applied techniques used for detecting pathogenic microorganisms that generally are based on plating, serological and biochemical assays are unreliable and expensive while lacking sensitivity and specificity compared to new analytical methods. Investigation of reliable and rapid analytical diagnosis methods seems a necessity today. In the present study, a high accurate method was developed aiming to pre-concentrate and improve identification of Staphylococcus aureus as a major bacterial human pathogen by using a molecular imprinted polymer (MIP) based membrane.
Materials and Methods: Cellulose acetate was used as the basic membrane with a pore size of 1.2 μm, methacrylic acid as the functional monomer, ethylene glycol dimethacrylate as the cross-linking monomer, antibody buffer medium as the template molecule, and 2,2'-Azobis(2-methylpropionitrile) as the initiator agent. After selecting the best membrane composition resulting from the optimum ratio of antibody to imprinted monomer, electron microscopy testing was used to evaluate the characterization and stabilization of the molecular imprinting of templates on the membrane.
Results and Conclusion: According to the results, the suspension of Staphylococcus aureus with a dilution of 3×105 after being adjacent to MIPs modified membranes had the highest bacterial mass absorption in MIP4 filter and reduced to a level of 1.3×104. The manufactured nano membrane could lead to a significant development in quality control of food industry compared to traditional methods due to a very shorter required time of bacterial mass diagnosis with a very higher accuracy.
Keywords: Antibody; Molecular Imprinted Polymer; Nano Membrane; Staphylococcus aureus
- ▪ Antibody ▪ Molecular imprinted polymer ▪ Nanomembrane ▪ Staphylococcus aureus
How to Cite
References
Ahmed A, Rushworth JV, Hirst NA, Millner PA. Biosensors for whole-cell bacterial detection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014;27:631-46. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00120-13.
Idil N, Mattiasson B. Imprinting of Microorganisms for Biosensor Applications. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland). 2017;17 (4):708. doi: 10.3390/s17040708
Roy E, Patra S, Tiwari A, Madhuri R, Sharma PK. Single cell imprinting on the surface of Ag-ZnO bimetallic nanoparticle modified graphene oxide sheets for targeted detection, removal and photothermal killing of E. Coli. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;89:620-26. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2015.12.085
Alexandre DL, Melo AMA, Furtado RF, Borges MF, Figueiredo EAT, Biswas A, Cheng HN, Alves CR. A Rapid and Specific Biosensor for Salmonella Typhimurium Detection in Milk. Food Bioproc Technol. 2018;11:748-56.doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-017-2051-8
Malvano F, Albanese D, Pilloton R, Di Matteo M, Crescitelli A. A New Label-Free Impedimetric Affinity Sensor Based on Cholinesterases for Detection of Organophosphorous and Carbamic Pesticides in Food Samples: Impedimetric Versus Amperometric Detection. Food Bioproc Technol. 2017;10:1834-43. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-017-1955-7
Kundu M, Prasad S, Krishnan P, Gajjala S. A Novel Electrochemical Biosensor Based on Hematite (α-Fe2O3) Flowerlike Nanostructures for Sensitive Determination of Formaldehyde Adulteration in Fruit Juices. Food Bioproc Technol. 2019;12:1659-71. doi: 10.1007/s11947-019-02318-7
Baker N, Greenway GM, Wheatley RA, Wiles C. A chemiluminescence nanosensor to monitor lipid peroxidation. Analyst. 2007;132:104-6. https://doi.org/10.1039/B615659B
Boysen RI, Schwarz LJ, Nicolau DV, Hearn MT. Molecularly imprinted polymer membranes and thin films for the separation and sensing of biomacromolecules. J Sep Sci. 2017;40:314-35. doi: 10.1002/jssc.201600849
Ahari H, Razavilar V, Akbari-Adergani B, Motallebi Moghanjoghi AA. Nanobiosensor designing with molecular framework polymer method compared with agent-linked nanosilica biosensor for Staphylococcus aureus exotoxin detection. Iran J Fish Sci. 2014;13:667-83.
Rezaei B, Khalili Boroujeni M, Ensafi AA. Caffeine electrochemical sensor using imprinted film as recognition element based on polypyrrole, sol-gel, and gold nanoparticles hybrid nanocomposite modified pencil graphite electrode. Biosens Bioelectron. 2014;60:77-83. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.03.028
Ben Aissa A, Herrera-Chacon A, Pupin RR, Sotomayor M, Pividori MI. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer for the isolation and detection of biotin and biotinylated biomolecules. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;88:101-08. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2016.07.096
Cáceres C, Bravo C, Rivas B, Moczko E, Sáez P, García Y, Pereira E. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for the Selective Extraction of Bisphenol A and Progesterone from Aqueous Media. Polymers. 2018;10. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10060679
Jia M, Zhang Z, Li J, Ma X, Chen L, Yang X. Molecular imprinting technology for microorganism analysis. TrAC-Trend Anal Chem. 2018;106:190-201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.07.011
Zhang W, She X, Wang L, Fan H, Zhou Q, Huang X, Tang JZ. Preparation, Characterization and Application of a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Selective Recognition of Sulpiride. Materials (Basel, Switzerland) 2017;10 (5):475. doi: 10.3390/ma10050475
Sobhan A, Oh JH, Park MK, Kim SW, Park C, Lee J. Assessment of peanut allergen Ara h1 in processed foods using a SWCNTs-based nanobiosensor. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2018;82:1134-42. doi: 10.1080/09168451.2018.1453295
Shen ZL, Yuan D, Su QD, Zhang H, Wang J, Zhu JH, Liu YM. Selective solid-phase extraction using molecularly imprinted polymer for analysis of methamidophos in water and soil samples. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2011;75:473-9.doi: https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.100668
Yang H-H, Zhou W-H, Guo X-C, Chen F-R, Zhao H-Q, Lin L-M, Wang X-R. Molecularly imprinted polymer as SPE sorbent for selective extraction of melamine in dairy products. Talanta. 2009;80:821-25. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2009.07.067
Holthoff EL, Stratis-Cullum DN, Hankus ME. A nanosensor for TNT detection based on molecularly imprinted polymers and surface enhanced Raman scattering. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland) 2011;11:2700-14. doi: 10.3390/s110302700
Zhang Z, Guan Y, Li M, Zhao A, Ren J, Qu X. Highly stable and reusable imprinted artificial antibody used for in situ detection and disinfection of pathogens. Chem Sci. 2015;6:2822-26.doi: 10.1039/c5sc00489f.
MansouriBoroujeni N. Development of a molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP)-based sensor platform for the fast and low-cost detection of yeast and pathogenic bacteria [Master's thesis (MSc) Manchester: Manchester Metropolitan University; 2017.
Okan M, Sari E, Duman M. Molecularly imprinted polymer based micromechanical cantilever sensor system for the selective determination of ciprofloxacin. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;88:258-64. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2016.08.047
Zheng L, Zhang C, Ma J, Hong S, She Y, Abd El-Aty AM, Yahui H, Yu H, Liu H, Wang J. Fabrication of a highly sensitive electrochemical sensor based on electropolymerized molecularly imprinted polymer hybrid nanocomposites for the determination of 4-nonylphenol in packaged milk samples. Anal Biochem. 2018;559:44-50. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2018.08.017
Pan J, Chen W, Ma Y, Pan G. Molecularly imprinted polymers as receptor mimics for selective cell recognition. Chem Soc Rev. 2018;47:5574-87. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CS00854F
Bole AL, Manesiotis P. Advanced Materials for the Recognition and Capture of Whole Cells and Microorganisms. Adv Mat (Deerfield Beach, Fla) 2016;28:5349-66. doi: 10.1002/adma.201503962
Shimamura Y, Hirai C, Sugiyama Y, Shibata M, Ozaki J, Murata M, Ohashi N, Masuda S. Inhibitory effects of food additives derived from polyphenols on staphylococcal enterotoxin A production and biofilm formation by Staphylococcus aureus. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2017;81:2346-52. doi: 10.1080/09168451.2017.1395681
Rezaei A, Pajohi-Alamoti MR, Mohammadzadeh A, Mahmoodi P. Detection of Gene Encoding Enterotoxin A in Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Cream Pastries. J Food Qual Hazards Control. 2018;5:24-28. doi:10.29252/jfqhc.5.1.24
Ahari H, Hedayati M, Akbari-adergani B, Kakoolaki S, Hosseini H, Anvar A. Staphylococcus aureus exotoxin detection using potentiometric nanobiosensor for microbial electrode approach with the effects of pH and temperature. Int J Food Prop. 2017;20:1578-87. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2017.1347944
Zelníčková J, Hutařová J, Vaculovičová M. Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Used for Staphylococcus aureus Isolation and Detection. Nanocon, Brno, Czech Republic, EU2019.
Zhang C, Zhong S, Yang Z. Cellulose acetate-based molecularly imprinted polymeric membrane for separation of vanillin and o-vanillin. Braz J Chem Eng. 2008;25:365-73. doi: https://doi.org/10.1590/S0104-66322008000200014
Akbari-adergani B, Sadeghian G-H, Alimohammadi A, Esfandiari Z. Integrated photografted molecularly imprinted polymers with a cellulose acetate membrane for the extraction of melamine from dry milk before HPLC analysis. J Sep Sci. 2017;40:1361-68. doi: 10.1002/jssc.201601245
Yang Y-z, Tang Q, Gong C-b, Ma X-b, Peng J-d, Lam MH-w. Ultrasensitive detection of bisphenol A in aqueous media using photoresponsive surface molecular imprinting polymer microspheres. New J Chem. 2014;38:1780-88. doi: 10.1039/C3NJ01598J
Ahmadi H, Javanbakht M, Akbari-adergani B, Shabanian M. Photo-grafting of β-cyclodextrin onto the polyethersulfone microfiltration-membrane: Fast surface hydrophilicity improvement and continuous phthalate ester removal. J Appl Polym Sci. 2019;136:47632. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/app.47632
Rajapaksha P, Elbourne A, Gangadoo S, Brown R, Cozzolino D, Chapman J. A review of methods for the detection of pathogenic microorganisms. Analyst. 2019;144(2):396-411.
Bursle E, Robson J. Non-culture methods for detecting infection. Australian prescriber. 2016 Oct;39(5):171.
Yan Y, Shi P, Song W, Bi S. Chemiluminescence and bioluminescence imaging for biosensing and therapy: in vitro and in vivo perspectives. Theranostics. 2019;9(14):4047.
Contag CH, Contag PR, Mullins JI, Spilman SD, Stevenson DK, Benaron DA. Photonic detection of bacterial pathogens in living hosts. Molecular microbiology. 1995 Nov;18(4):593-603.
Selan L, Berlutti F, Passariello C, Thaller MC, Renzini G. Reliability of a bioluminescence ATP assay for detection of bacteria. Journal of clinical microbiology. 1992 Jul 1;30(7):1739-42.
Turner DE, Daugherity EK, Altier C, Maurer KJ. Efficacy and limitations of an ATP-based monitoring system. Journal of the American Association for Laboratory Animal Science. 2010 Mar 15;49(2):190-5.
- Abstract Viewed: 360 times
- pdf Downloaded: 455 times
