Isolation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) from Wharton’s Jelly (WJ) Tissue of Human Umbilical Cord (hUC); a Protocol
Student Research in Translational Medicine,
Vol. 5 (2023),
30 December 2023
https://doi.org/10.22037/smsj.v5.42169
Abstract
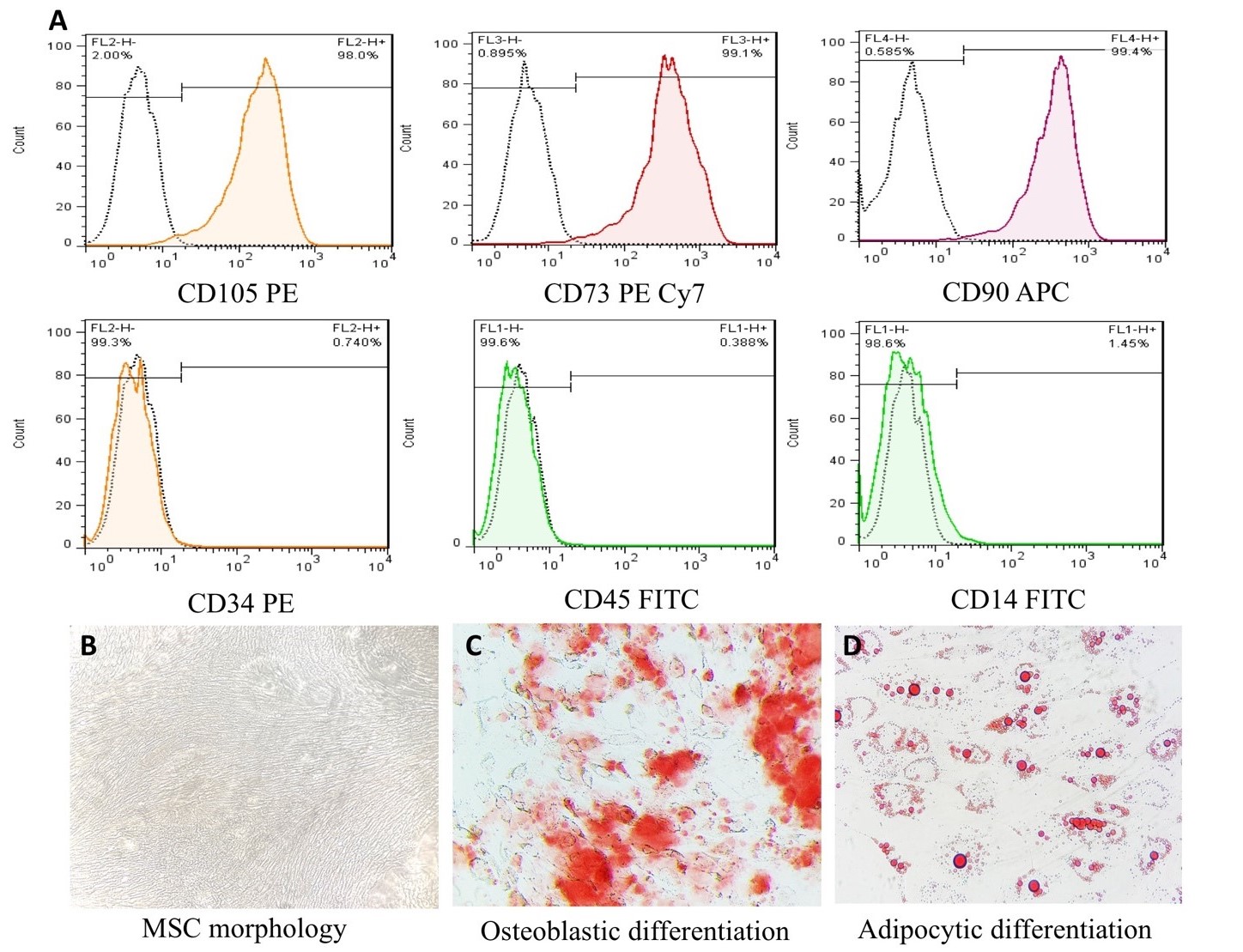
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) with their spindle like shapes are a lineage of stem cells with the capacity to self-renew and differentiate into osteoblasts, adipocytes, and chondrocytes and with CD105, CD73, and CD90 expression and the lack of CD34, CD14, CD45, and HLA - DR expression. The immunomodulatory, angiogenic, antiapoptotic, antimicrobial, and antioxidative characteristics of these cells made them more attractive in the field of cell - therapy for several autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, including diabetes, neurological disorders, sepsis, cardiac ischemia, and GvHD. For this reason, various protocols have been proposed to isolate mesenchymal stem cells from different tissue sources, such as adipose tissue (AT), umbilical cord (UC), Wharton’s jelly (WJ), bone marrow (BM), dental pulp, and even menstrual fluid. Considering the ease of access to the umbilical cord tissue and the fact that this tissue is rich in MSCs with embryonic origin and higher proliferation rate and lower senescence of the cells, the umbilical cord became a suitable source for explant MSC culture. In this study, we decided to introduce an explant culture protocol of MSCs that is less expensive and cost - effective achieving a high yield of MSCs.
- Mesenchymal Stem Cell
- Wharton Jelly
- Umbilical Cord
- Primary Cell Culture
- Cell Culture Techniques
How to Cite
References
Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, Slaper-Cortenbach I, Marini FC, Krause DS, et al.Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement.Cytotherapy.2006;8(4):315-17.
Berebichez-Fridman R and Montero-Olvera PR.Sources and Clinical Applications of Mesenchymal Stem Cells: State-of-the-art review.Sultan Qaboos University Medical Journal.2018;18(3):e264-77.
Vieira Paladino F, de Moraes Rodrigues J, da Silva A and Goldberg AC.The Immunomodulatory Potential of Wharton’s Jelly Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells.Stem Cells International.2019;2019:3548917.
Munoz-Perez E, Gonzalez-Pujana A, Igartua M, Santos-Vizcaino E and Hernandez RM. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Secretome for the Treatment of Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases: Latest Trends in Isolation, Content Optimization and Delivery Avenues. Pharmaceutics2021.
Műzes G and Sipos F. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Secretome: A Potential Therapeutic Option for Autoimmune and Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases. Cells2022.
Eleuteri S and Fierabracci A. Insights into the Secretome of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Its Potential Applications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences2019.
Chen J-Y, Mou X-Z, Du X-C and Xiang C.Comparative analysis of biological characteristics of adult mesenchymal stem cells with different tissue origins.Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine.2015;8(9):739-46.
Davies JE, Walker JT and Keating A.Concise Review: Wharton's Jelly: The Rich, but Enigmatic, Source of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells.Stem Cells Translational Medicine.2017;6(7):1620-30.
Elahi KC, Klein G, Avci-Adali M, Sievert KD, MacNeil S and Aicher WK.Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells from Different Sources Diverge in Their Expression of Cell Surface Proteins and Display Distinct Differentiation Patterns.Stem Cells International.2016;2016:5646384.
Kwon A, Kim Y, Kim M, Kim J, Choi H, Jekarl DW, et al.Tissue-specific Differentiation Potency of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells from Perinatal Tissues.Scientific Reports.2016;6(1):23544.
Varaa N, Azandeh S, Khodabandeh Z and Gharravi AM.Wharton’s Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cell: Various Protocols for Isolation and Differentiation of Hepatocyte-Like Cells; Narrative Review.Iranian Journal of Medical Sciences.2019;44(6):437-48.
Deuse T, Stubbendorff M, Tang-Quan K, Phillips N, Kay MA, Eiermann T, et al.Immunogenicity and Immunomodulatory Properties of Umbilical Cord Lining Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Cell Transplantation.2011;20(5):655-67.
Wang Q, Yang Q, Wang Z, Tong H, Ma L, Zhang Y, et al.Comparative analysis of human mesenchymal stem cells from fetal-bone marrow, adipose tissue, and Warton's jelly as sources of cell immunomodulatory therapy.Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics.2016;12(1):85-96.
Yoon JH, Roh EY, Shin S, Jung NH, Song EY, Chang JY, et al.Comparison of Explant-Derived and Enzymatic Digestion-Derived MSCs and the Growth Factors from Wharton’s Jelly.BioMed Research International.2013;2013:428726.
- Abstract Viewed: 162 times
- PDF Downloaded: 105 times




